Coalition's 'request for information' system in the spotlight in light of New York Times document release
For many years during the international air campaign against the so-called Islamic State (ISIS), Airwars participated in information sharing with the US-led Coalition on civilian harm incidents. When local Syrian and Iraqi sources alleged civilians had been killed or injured, the Coalition would review the event and on occasion ask Airwars for specific details. These official Requests for Information (RFIs) ranged from seeking the coordinates of a specific building, to requesting details about how many civilians died in particular strikes or neighbourhoods.
Airwars’ team would then pore over our own archives; geolocate events by exploiting every piece of known information; and then send back a detailed response. While there were periods when our public relations with the Coalition were fraught, we continued to work privately with its civilian harm assessment team over several years, in the hope that our technical assistance would lead to more recognition of civilian harm.
Yet a newly published trove of more than 1,300 previously classified military assessments, released by The New York Times after a lengthy lawsuit, has highlighted that the US-led Coalition’s internal reporting processes for civilian harm were often defective and unreliable. This, The Times claims, led the Coalition to radically underestimate the number of Syrian and Iraqi civilians it killed.
Those 1,300 assessments of civilian harm also provide an opportunity to assess how the Coalition itself carried out the RFI process.
Airwars selected a sample of 91 incidents between December 2016 and October 2017. In each case, the US-led Coalition had specifically reached out to Airwars requesting further details on alleged civilian harm. In 70 of these cases, we were able to match our response directly to declassified assessments in the Times database.
The results are concerning.
In total, in only three of the 70 cases where the Coalition asked Airwars for more information did it eventually go on to accept causing civilian harm. The other 67 incidents were deemed ‘non-credible.’
In 37 of the cases we were able to provide exactly the information they requested. In the other 33 cases we provided as much as possible, often including specific locations and details on victims.
Airwars’ monitoring has found that at least 8,168 civilians have been killed by the US-led Coalition during the campaign against ISIS. The Coalition, however, has accepted responsibility for 1,417.
‘No specific information’
We identified three worrying trends in how our information was treated during the RFI process. The first was that the Coalition sometimes closed assessments before we had even provided our feedback, or did not reopen them when new information was provided.
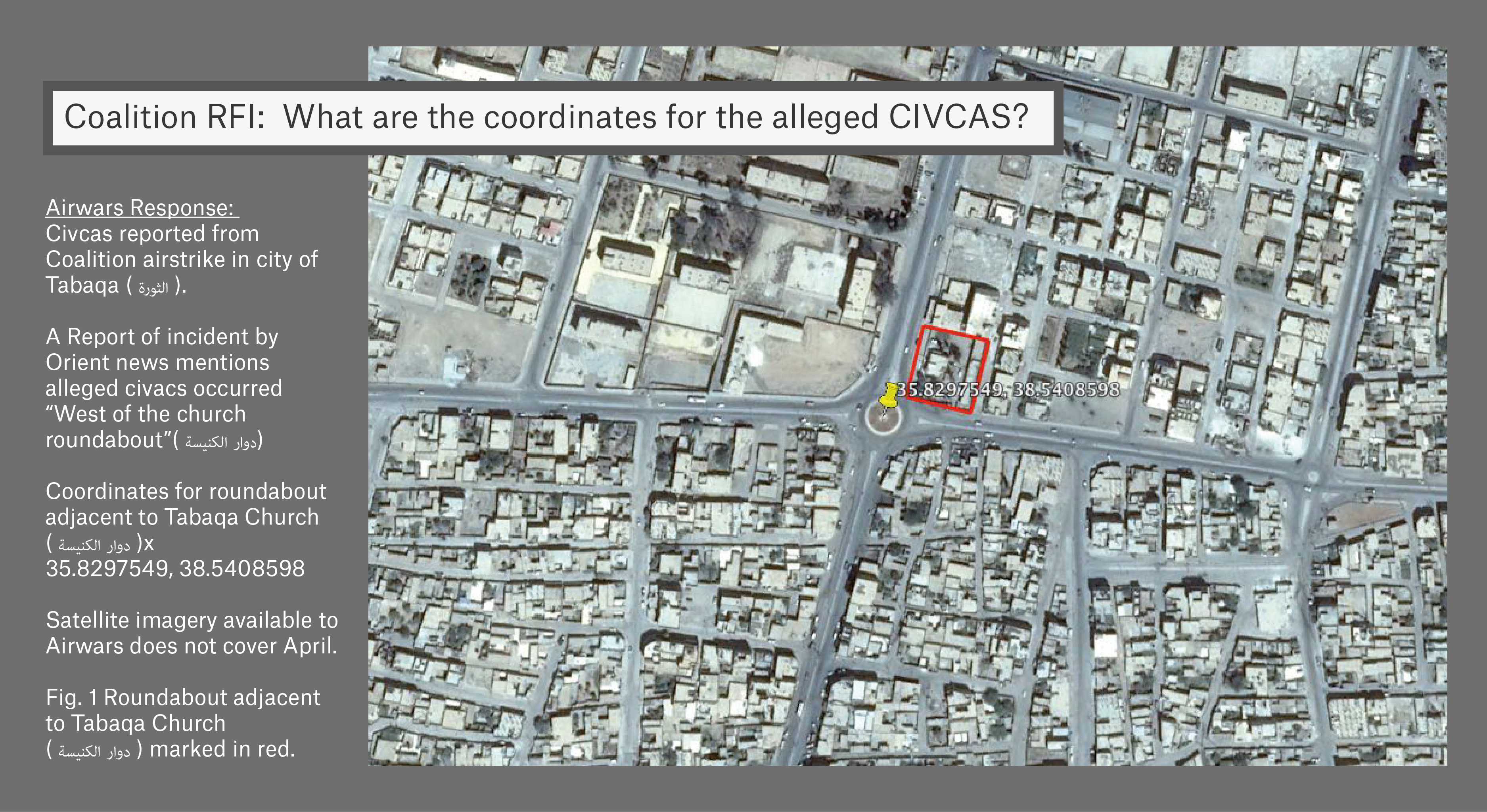
On April 30th, 2017, three civilians were reportedly killed in an apparent airstrike near a roundabout in Tabaqa in western Raqqa province, Syria, with up to eighteen more people wounded. All sources attributed the attack to the US-led Coalition that was, at the time, involved in one of the most intense stretches of its grinding campaign against ISIS – striking dozens of targets a day.
The three civilians who died were reportedly women, although their identities remain unknown. Ongoing fighting in the area had led to mass displacement of civilians and the ones who stayed behind were often trapped between ISIS and the US-led Coalition. Local sources reported the attack had hit a civilian neighbourhood near the ‘church roundabout.’
In the middle of 2017, Airwars wrote to the Coalition raising concerns about this incident.
Later that year, the Coalition opened up an initial assessment on the event. Its own civilian casualty assessment team wrote to Airwars on November 22nd with a simple question: “What are the coordinates for the alleged CIVCAS?”
Shortly afterwards, Airwars provided close coordinates for the event to the Coalition following work by our own geolocations team as documented below.
We also included a satellite image of the likely location – a 350 x 260m area north east of the roundabout.
Yet we now know that some time before our email was sent, the Coalition had privately deemed the event to be ‘non-credible’. It asserted that the claim needed to “be more specific to justify performing a search for strikes.”
Even after receiving Airwars’ response, there is no evidence the case was reopened. A year later, a press release declared that there was “insufficient information of the time, location and details to assess its credibility.” To date the US-led Coalition still does not accept responsibility for the deaths of those three women.
In total we tracked at least 18 such cases where the Coalition had already closed case files before we had responded. In none of these cases was there any evidence they reopened the file.
A second dispiriting trend was how rarely Airwars’ work actually prompted further review by the Coalition.
As the New York Times files show, the vast majority of Coalition probes stopped at the initial assessment stage – essentially a series of yes/no boxes where a single ‘no’ leads to the allegation being deemed ‘non-credible.’ In only seven of the 70 cases where we provided information did this lead to additional review steps being taken – in most cases turning an initial assessment into a Civilian Casualty Assessment Report (CCAR). These are slightly longer assessments but again often end in non-credible determinations.
If the evidence is more significant – or if there are claims of a breach of the laws of war – a third, far more extensive, investigation called an AR15-6 could be carried out. We did not find any cases in the sample that went as far as an AR15-6, even among the three cases deemed credible by Inherent Resolve.
‘Thicker walls’
A third trend was that in cases where Airwars itself was not able, from local reporting, to specify exactly which civilians were killed in particular locations, the Coalition almost always rejected such allegations.
Particularly during intense urban fighting, local reports of civilian harm often comprise casualties from a number of weapon releases across an area over a period of time, which can make it difficult to ascertain the exact location where each victim was harmed. This would have been especially challenging during 2017, the most intense year of bombing in Iraq and Syria, when the sheer number of Coalition strikes made allegations even harder to disentangle.
When a few incidents were reported in the same area, the Coalition would often request that we specify which civilian harm occurred in which location. In 15 cases, the Coalition decided that, rather than search multiple areas they would instead close the assessment, using justifications such as “the CIVCAS numbers need to be broken up into the neighbourhoods that they belong to.”
A typical case was the strikes on January 3rd 2017 which killed up to 22 civilians and injured 29 more in eastern Mosul, reportedly targeting two houses close together. Two children were among those reported killed. Only one of the fatal victims – Younis Hassan Abdullah al-Badrani – was named in reports.
An RFI sent by Coalition assessors asked Airwars which civilian casualties were attributed to which of three named neighbourhoods in Mosul – Mushayrifa, Hermat, Ma’moon. We replied back with the exact time and coordinates of an airstrike in Ma’moon, although we also noted that sources did not differentiate between the three proximate neighbourhoods when attributing civilian casualties. The corresponding document published by the New York Times shows the Coalition investigation was then closed and deemed ‘non-credible’ on the grounds that there were no Coalition strikes in Mushayrifa, even though we had provided an exact location in Ma’moon. It’s unclear whether the Coalition assessors ever investigated all of the three neighbourhoods identified.
Other claimed civilian harm events were closed despite there being credible information provided not just by Airwars, but also in detailed investigations by other major NGOs – such as an airstrike on April 28th 2017, where multiple members of two families were killed in a residential home on Palestine Street in Tabaqa, Syria.
Fifteen members of the Dalo family, including five children under the age of ten, and three members of the al Miri’i family, were killed by a suspected Coalition airstrike at 4pm. A Human Rights Watch investigation released months later spoke to the owner of the house that had been flattened, who said he had given the Dalo family his keys as his house had thicker walls than their own. HRW also found the remnants of a Hellfire missile at the scene – which was linked back to Lockheed Martin, one of the US military’s largest contractors.
Despite this wealth of evidence, the US-led Coalition maintained there was insufficient information about the location, time and date – despite Airwars providing coordinates for the district that Palestine Street was in, as close as we could get with limited satellite imagery. Airwars also provided an exact date for the incident, as Coalition assessors were unsure about whether this incident took place on April 28th or May 3rd. After speaking directly with local sources, Airwars determined that the incident took place on April 28th, although cleanup efforts led to bodies being pulled from the rubble several days later.
None of this detailed information appeared to influence the Coalition – which deemed the event ‘non credible.’
How it should work
Our limited review of the Times documents did reveal at least one instance where Airwars provided information which then helped change the internal designation of an incident from non-credible to credible. This, in theory, was how the system was meant to operate.
On March 21st 2017, between 10 and 20 civilians were reported killed and dozens more injured when Coalition airstrikes targeted multiple locations in Tabaqa, Syria. A number of buildings, including a gas depot, a carwash, garages, shops and the area around the hospital were reportedly damaged.
In October, the Coalition asked Airwars for the locations of each of these sites. We provided exact coordinates for the majority, while providing neighbourhood-level coordinates for the remainder, alongside annotated satellite imagery.
Unusually, the Coalition then used this information to review its own strike database. Three corroborating strikes were identified, of which two were assessed to have led to civilian harm – one death and one injury. However, even here, the extent of the Coalition’s admission starkly contrasts with the number of fatalities and injuries reported by local sources. While the Coalition assessment claims it is ‘more likely than not’ that one civilian was killed and another injured as a result of these strikes, local sources insisted that between 10-20 civilians were killed, and up to 36 more injured in the same incident.
This RFI response by Airwars appears to have been no more or less remarkable than the other 36 cases where we provided the Coalition with exact information as requested. Yet it is the exception in terms of the event being officially deemed credible.
Were the Coalition to have treated those other 36 cases in the same manner, it might have accepted responsibility for at least 50 more civilian fatalities. Instead these civilians remain uncounted, and their families’ questions unanswered.
“We are only beginning to get to grips with this vast trove of formerly secret Coalition assessments – yet what we are finding already troubles us deeply,” says Airwars research manager Emily Tripp. “Iraqis and Syrians deserve far better than the inconsistencies, poor work and disinterest in casualty estimates which are demonstrated, again and again, by these official documents.”