In November 2023, Airwars and Article 36 co-convened a workshop to explore military perspectives on the opportunities and challenges arising in the implementation of the Political Declaration on Strengthening the Protection of Civilians from the Humanitarian Consequences Arising from the Use of Explosive Weapons in Populated Areas.
In the workshop report, we summarise the discussions held and challenges identified during the two-day workshop. We draw on these lessons, and our wider work on EWIPA, to make recommendations to states and militaries working to implement the declaration, and civil society organisations focused on supporting this process.
The workshop focused on exploring operational policies and practice regarding the use of explosive weapons during military operations in populated areas, with reference to the Declaration. Using a scenario-based approach, the workshop aimed to identify, and raise awareness of, changes to policies and practices that are necessary for the effective implementation of the operational provisions of the Declaration, ahead of the first official follow-up meeting of states and civil society which will be held in Oslo next week.
Participants in the workshop included active and retired members of national armed forces and defence ministry officials from 8 Western states, as well as participants from NATO, the International Committee of the Red Cross (ICRC), and civil society organisations.
Key findings
A summary of the key recommendations and good practices outlined during the workshop are summarised below:
-
Efforts to disseminate and promote engagement with the Declaration at the national level are required within relevant ministries and departments as well as the armed forces.
A process of policy review, revision and development by signatory states is an essential element of the implementation process.
To promote and implement the Declaration, it is vital to include both leaders at the strategic/political level as well as commanders at the operational level.
Commanders have a key role to play in ensuring civilian harm is mitigated, particularly from the use of explosive weapons in populated areas.
The Declaration’s central commitment points towards national-level policies and doctrines as the framework through which it should be implemented.
Weapon selection, including a proper understanding of the technical effects of different weapons and how those effects will be influenced by the built environment, is critical to mitigating civilian harm from explosive weapons.
States should critically review their approaches to and capacity for undertaking civilian harm tracking in line with established good practice.
The full workshop report can be found here.
Airwars data featured in detailed visual breakdown by The Sunday Times
This article was originally published in The Sunday Times after Airwars worked with their team to visualise the patterns of families killed in our archive of civilian harm in Gaza. The introduction is repeated below but the entire article is available here, and an archived version here.
Maisara al-Rayyes was in the prime of his life. At 30, he had just completed his medical studies at King’s College London as part of the prestigious Chevening scholarship, which brings “outstanding emerging leaders” to study in Britain, funded by the Foreign Office.
Returning to Gaza last summer to work with Doctors Without Borders, he married a fellow scholar, Laura Hayek, whom he described as “the most gorgeous and kind-hearted girl” he had ever met.
A social media post on September 12 shows him taking a selfie with James Cleverly, the foreign secretary, after al-Rayyes and other scholars were invited to discuss the challenges and aspirations of young Palestinians.
Two months later he and his entire family were killed.
The al-Rayyes family are one of at least 1,800 that the Gazan authorities say have lost multiple members. In some cases whole families are being erased, their surnames removed from the civil registry, the official government record of citizens.
In collaboration with Airwars, the British-based organisation that counts civilian casualties in conflicts around the world, The Sunday Times has collated the details of more than 150 families that have lost multiple members in the Israel-Gaza war.
These are some of their stories.
Share on
At least 127 civilian harm allegations in 'safe zone' in first week after evacuation order
Airwars’ investigator Sanjana Varghese spoke to NPR’s Ruth Sherlock about this investigation. You can read the article here.
On October 12th, the Israeli military issued a blanket call for all Palestinians living in the north of the Gaza strip to move south, saying it was “for your own safety”. More than one million people were told to flee, ahead of an expected ground invasion.
The evacuation zone started at Wadi Gaza, which runs through the centre of the Gaza Strip. In theory, civilians fleeing south of that line should have been safer, but Palestinians have reported extensive attacks in civilian areas in the central and southern parts of Gaza.
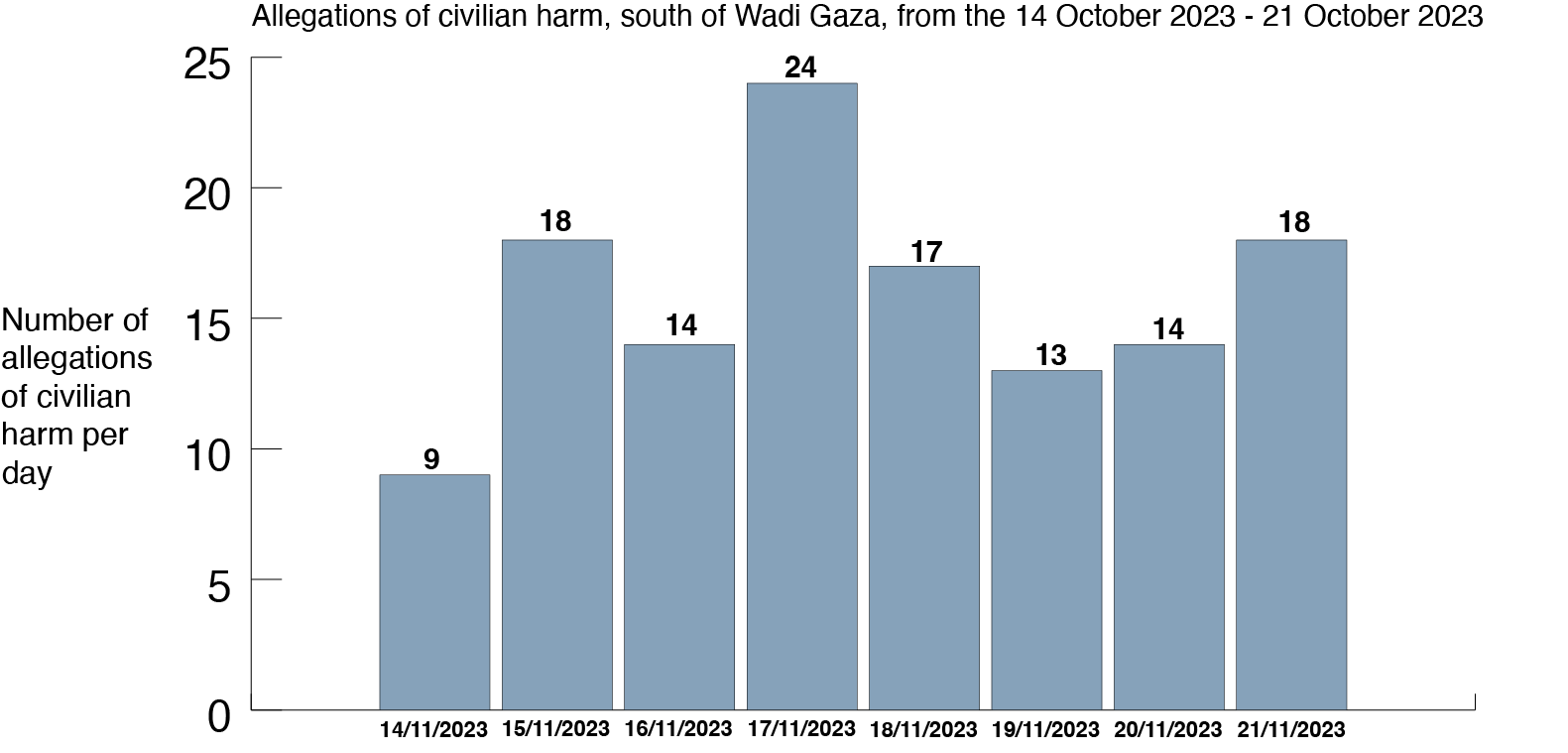
In the first seven days after the warning – from October 14th to 21st – Airwars’ investigation team tracked and geolocated at least 127 separate allegations of civilian harm from explosive weapons in this southern zone.
Amongst these strikes were many that allegedly hit densely populated neighbourhoods and civilian objects such as schools, hospitals and restaurants. The frequency of these allegations in this supposed safe zone suggests that there was no safe place for civilians in Gaza, despite assurances from Israeli authorities.
Safe to flee?
On October 7th, 2023 Hamas militants broke through the fence that separates Gaza from Israel and killed more than 1,000 people, according to Israeli authorities. In retaliation Israel has dropped thousands of bombs on Gaza ahead of a ground invasion, killing more than 10,000 people, according to Palestinian authorities.
Since October 7th, Airwars’ research team has been tracking every public allegation of civilian harm in order to provide an independent assessment of civilian casualties.
We have already tracked more than 1,000 separate allegations across the Gaza Strip alone; each allegation represents the death or injury of at least one civilian resulting from explosive weapons use. For the most part, these allegations are still being fully assessed by our research team – with additional sources identified, casualty ranges produced, and where possible details on civilian names and biographies captured. You can find full details of the around 40 published incidents here, and more about our methodology here.
But we have also been able to use these allegations to understand overall patterns of harm. By geolocating each harm claim from the week following the IDF’s instructions for civilians to move south, we have been able to pull together a comprehensive database of 127 likely Israeli strikes leading to allegations of civilian harm that occurred the week following the evacuation order. An allegation of civilian harm does not mean that just one civilian was injured or killed; these allegations often involve multiple people, as well as damage to buildings or family homes.
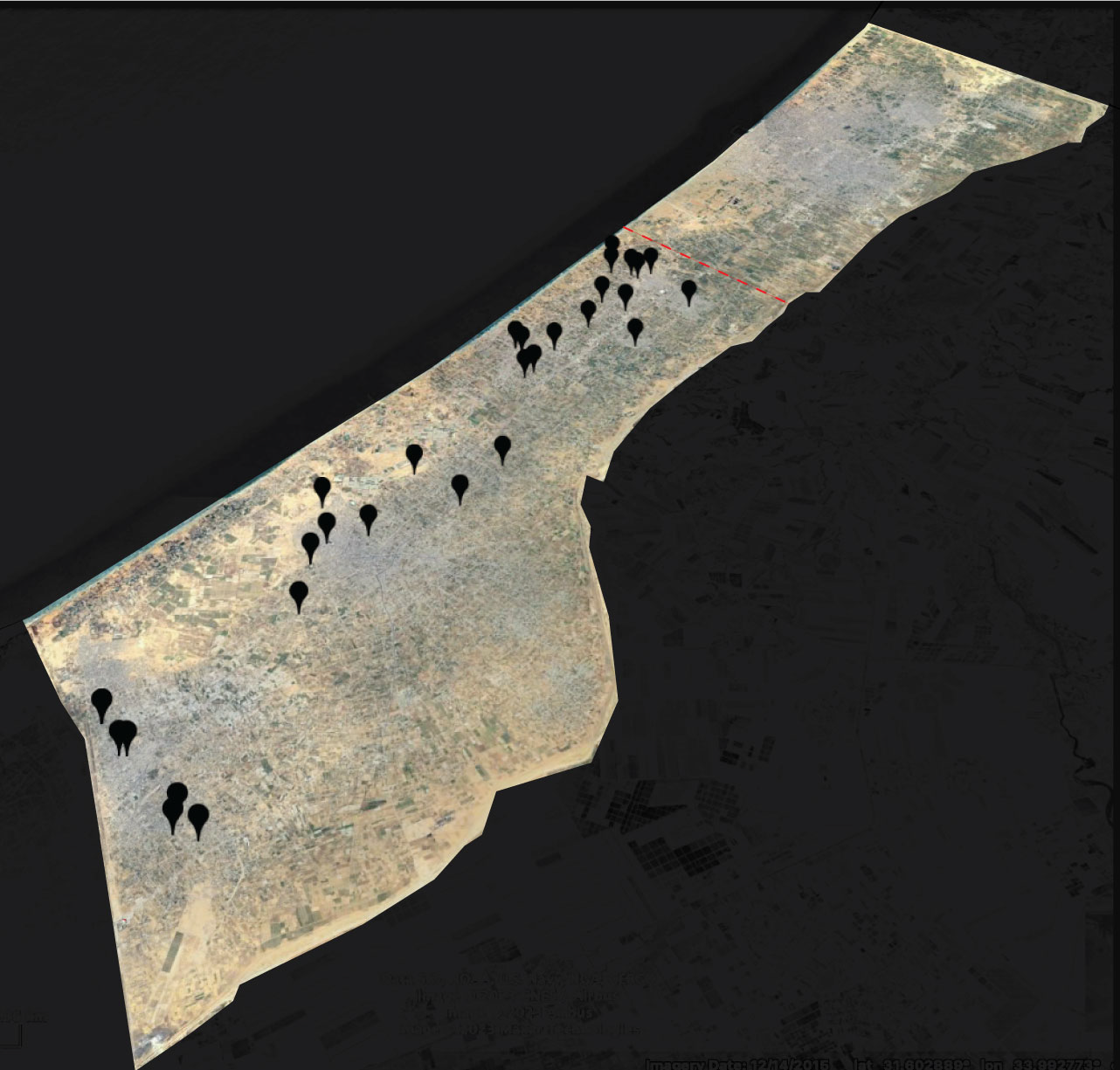

Map of civilian harm allegations, south of Wadi Gaza, between 14-21 October 2023. The red dotted line refers to the Wadi Gaza. Many locations include more than one alleged civilian harm incident. Sanjana Varghese / Airwars. Images via Maxar Technologies / Airbus / Google Earth.
We relied on news reporting, humanitarian agencies and organisations, open source documentation and relevant footage where necessary. We geolocated allegations to six levels of accuracy: area/region, neighbourhood, landmark/building, hospital, street, and an exact location. Any alleged civilian harm incident that we couldn’t geolocate was discounted from our dataset.
The distance from the Wadi Gaza to the Rafah Border Crossing on the southern border of the Gaza strip is roughly 27 kilometres. From east to west across the Gaza strip, the distance is around 6 kilometres at the narrowest point, and 12 kilometres at its widest point.
We found harm allegations on every day following the evacuation order. Just four days after the south was declared to be a safe area, the most civilian harm allegations were documented: twenty four allegations, suggesting at least twenty strikes in an area little longer than Manhattan.
In incidents that have been fully researched by Airwars’ research team, we found that in some cases strikes affected whole families as they sheltered together. In one incident, on October 21st, 2023, an alleged Israeli strike hit a Palestinian civil defence facility, alongside the Dahir family home, in Khirbet-al-adas, Rafah. Between six and ten people were likely killed in this strike and up to 11 injured. Of those killed, at least five were children from the same family, all aged 13 and under. Airwars assessors were able to cross-reference six of the individuals in this assessment with the dataset of names and individual ID numbers released by the Palestinian Ministry of Health (MoH).
In another incident on October 15th, in the al-Geneina neighbourhood in Rafah, the home of a doctor, Dr. Salah al-Din Zanoun, was hit. There were likely seven to eight people killed, all of whom were from the same family. Of those killed, Airwars assessors were able to cross-reference five of the individuals in this assessment with the dataset of names and individual health ID numbers released by the MoH.
We also found that multiple civilian objects – such as hospitals and schools – were hit in the south of Gaza. As people were told to move south – and around 700,000 people, according to the New York Times, did so initially – many took shelter in buildings such as hospitals and schools. In a number of cases large numbers of civilians were crowded together when strikes hit this infrastructure, such as a strike on a UNRWA school in al-Maghazi refugee camp, on October 17th. UNRWA said that around 4,000 people were sheltering at this school. The next day, an alleged airstrike hit another UNRWA school in Khan Younis – footage from the immediate aftermath clearly showed that groups of people had been using the school as a home, with clothes laid out over external railings around the school.
The scale of this campaign in Gaza makes this one of the most intense conflicts that Airwars has ever monitored – in just the first three weeks of the war, we monitored more individual incidents of harm than in any given month of any conflict Airwars has monitored: including deadly campaigns such as the war against ISIS. Our data also suggests that civilian harm is being compounded by the deteriorating conditions for civilians in Gaza, which is already one of the most densely populated areas in the world.
Clarifying note
Airwars uses a grading system to assess our allegations of civilian harm (you can read more about this here). Our assessments are being published in batches once they have been through the full review process.
Airwars has only tracked allegations of civilian harm – this means that there may be attacks with no public allegations of civilian harm which we haven’t included in our dataset.
Share on
Israel and Gaza 2023
Forensic analysis and expert analysts suggest Israeli strike likely cause
This article was originally published in the Financial Times and written by the paper’s correspondents, as well as Airwars’ Joe Dyke and Nikolaj Houmann Mortensen. The full article can be read here.
Just a day after Israel ordered 1.1 million civilians to leave northern Gaza, two blasts on Friday destroyed multiple cars driving along one of the enclave’s main roads south.
Videos of the aftermath verified by the Financial Times show 12 bodies of men, women and children in Salah-ad-Din street, which Israel later designated a ‘safe route.’ One of the explosions rocks an ambulance as it attempts to leave the scene with some of the injured.
To assess the competing claims, the FT worked with Airwars, a conflict monitoring group, as well as munitions experts to shed light on the nature of the attack, its timing, aftermath and type of explosive used.
An overview of the actions needed
On Friday November 18th, states and civil society joined together in Dublin Castle to officially endorse the long-awaited international Political Declaration on the use of explosive weapons in populated areas (EWIPA). So far, 82 states have signed onto the declaration; this is a similar number to the initial signatories to other international declarations that have created new norms and standards in warfare, such as the Safe Schools Declaration. Among the signatories to the EWIPA declaration are states such as the US, UK, Netherlands, and Belgium, all of which made sizable contributions to the coalition against ISIS in Iraq and Syria that killed an estimated 8,194–13,249 civilians.
According to Action on Armed Violence, when EWIPAs are used, over 90% of those harmed are civilians. Airwars recently put together a series of maps showing the clear and troubling connection between population density in cities and civilian deaths during urban warfare. Even beyond those who are killed immediately, the reverberating effects are often severe and pervasive, with schools, hospitals, livelihoods, and basic resources like food and water becoming inaccessible for years. This has played out in recent conflicts in cities such as Mosul and Raqqa, in which entire city parts were destroyed and have been made uninhabitable.
The Irish-led, UN backed international declaration is a groundbreaking step towards curbing the use of such weapons. It comes at the back of a decade of civil society focus and pressure on this, led by the INEW network, which Airwars is a part of. As with any political declaration, the results are only as good as the implementation. Below, we outline some of the challenges states must address as they begin the process of implementing the EWIPA declaration.
States must be frank about gaps in their current approach
The first step in understanding how to implement the declaration to limit the use of EWIPAs must be for each state to critically examine current gaps in its own approach and engage in a meaningful process to address these. This in itself might be a stumbling block for some; while states such as the US and the Netherlands have shown increasing willingness to address gaps in their approach to the protection of civilians by working with civil society and experts, others have not.
The UK for instance, still falls behind allies in terms of transparency on evidence collection around civilian harm. Under the declaration, states committed to: “Collect, share, and make publicly available disaggregated data on the direct and indirect effects on civilians and civilian objects of military operations involving the use of explosive weapons in populated areas, where feasible and appropriate”. Despite the UK representative in Dublin noting during the signing ceremony that “the UK already has policies and procedures in place to support the implementation”, this has to date not been evident when it comes to public reporting on the effects of UK military actions.
As it stands, the UK maintains that it has evidence of only a single civilian casualty from its actions in the seven year anti-ISIS campaign, for example, despite extensive military involvement. The US, by comparison, has admitted to over 1,400 civilian casualties as part of the Coalition. When challenged, UK officials tend to emphasise that they are aware that is not a case of lower civilian casualties than in previous conflicts – but of poor evidence gathering. This position was summarised by former Armed Forces Minister, Mark Lancaster, who emphasised in 2019 that; “[I]t is not our position that there has been only a single civilian casualty as a result of our military action. What we are saying is that we have evidence of only a single, or what we believe to have been a single, civilian casualty.”
In spite of this oft-repeated recognition that the evidence gathering mechanisms of the UK are not able to accurately reflect the reality on the ground, there is, to our knowledge, no process in place to improve this approach and little willingness to engage with civil society to address this. If this is not addressed, there will be a significant gap between the rhetoric of UK leadership when it comes to EWIPA and the reality on the ground.
States must build clarity on who is responsible for implementing the EWIPA declaration on a national level
The second step states must take to implement the EWIPA declaration is to gain better internal understandings of who will be involved in its implementation. This must include those focusing specifically on EWIPA, but also those focusing on topics such as human security, the protection of civilians, humanitarian response, development, diplomacy, and all the other elements required to protect those caught in conflict from being harmed by explosive weapons.The structures behind overseas military engagements are complex, quick changing, and lines of responsibility are often murky. Yet it is only if all involved in such operations, across parliament, ministries of defence, and ministries of foreign affairs and overseas development, are dedicated to limiting the use of EWIPA, understanding their impact, and tracking civilian harm that occurs if they are used, that implementation will be effective.
States must be open to civil society inclusion in the implementation of the EWIPA declaration
Civil society actors, many of us united under the INEW banner, played a significant role in the development of the EWIPA declaration and the advocacy that brought states to the process, a fact that was acknowledged by a large number of states at the conference in Dublin. We stand ready to support the implementation in national contexts and across international coalitions. Many civil society organisations have spent years – sometimes decades – developing protection mechanisms and civilian harm tracking mechanisms, as well as conducting research into valuable lessons on the impact of EWIPA. Civil society organisations are also often direct links to the communities affected. It is in all of our interests that these resources are effectively shared with those in power.
In those states where there is a history of poor transparency and accountability on civilian harm and civilian harm tracking, governments and their militaries must also commit to a certain level of transparency on the implementation of the EWIPA declaration. They should work with civil society actors to understand the gaps in their current approach and set up milestones for implementation.
Looking forward
The endorsing ceremony was a promising step towards recognising the immense harm that these weapons have caused in recent years – and the harm they will continue to cause as their impact reverberates through communities. If the declaration is implemented well, fewer civilians will be harmed by explosive weapons in their cities, towns, and camps.
Yet there are pitfalls each state must avoid if their implementation of the declaration is to be meaningful. They must be frank about current gaps in their system and must be willing to address them. They must gain an oversight of everyone who will play a role in the effective implementation of EWIPA. And they should work with civil society actors who have resources to share and stand ready to support implementation.
Additional resources:
-
Implementation Brief: Political Declaration on the Use of Explosive Weapons in Populated Areas, CIVIC, November 2022 (here)
Safeguarding Civilians: A Humanitarian Interpretation of the Political Declaration on the Use of Explosive Weapons in Populated Areas, Human Rights watch and the International Human Rights Clinic at Harvard Law school, October 2022 (here)
Implementing the Political Declaration on the Use of Explosive Weapons in Populated Areas: Key Areas and Implementing Actions, INEW and Article 36, November 2022 (here)
Over 80 Countries Committed to Curb Use of Explosive Weapons, Now Comes the Hard Part, Bonnie Docherty, Human Rights Watch for Just Security, November 23rd 2022 (here)
Number of civilians killed decreases across monitored conflicts, while focus on explosive weapons use grows
Civilian harm dropped across most of the major conflicts in the Middle East and North Africa in 2021, Airwars’ annual report has found.
The number of allegations of civilians killed by nearly all belligerents monitored by Airwars fell in Syria, Iraq, Libya, Somalia and Yemen, though there was an escalation in the Israel-Palestinian conflict which caused significant human suffering.
Read Airwars’ full annual report here
US actions decline
The United States, which has fought multiple campaigns across the Middle East, Africa and Central Asia over the past two decades, saw a significant decrease in its activities.
Across all the US campaigns Airwars monitors, including in Syria and Iraq, as well as counterterrorism campaigns in Yemen, Somalia and elsewhere, civilian harm from US actions fell in 2021, continuing a downward trend in recent years.
In Iraq there were no reports of civilian harm from US actions, while in Syria at least 15 and up to 27 civilians were likely killed by US-led Coalition actions in 20 incidents throughout the year – mostly in combined air and ground actions that appeared to target alleged remnant ISIS fighters.
In Yemen at least two civilians were reportedly killed by US strikes during the year while there were no reliable local allegations of civilians likely killed by US strikes in Libya or Pakistan, according to Airwars’ assessment of local sources.
Even taking into account hundreds of airstrikes in Afghanistan which both the Trump and Biden administrations had initially kept secret, 2021 saw the lowest numbers of declared US military strikes globally since 2006.
However, 2021 was also a year in which focus was again placed on civilian harm caused by historic US actions.
To mark the 20th anniversary of the 9/11 terrorist atrocities, Airwars conducted an investigation to estimate how many civilians were likely killed by US forces alone in the subsequent 20 years of the so-called War on Terror. The research concluded that an estimated 22,000 to 48,000 civilians had been killed directly by US actions in two decades of war according to public records – the vast majority of fatalities were in Afghanistan, Iraq and Syria. The findings were cited in the opening remarks of the Senate Judiciary Committee hearing “’Targeted Killing’ and the Rule of Law: The Legal and Human Costs of 20 Years of U.S. Drone Strikes,” and were covered by more than 60 news outlets globally, in at least ten languages.
The Pentagon’s troubling management of civilian harm allegations was highlighted by another Airwars investigation during 2021, leading the Pentagon to withdraw and republish their own annual report to Congress. Airwars uncovered nine historic incidents in Iraq and Syria that the US had declared responsibility for killing civilians in, which were actually conducted by US allies including Australia, France, the United Kingdom and Belgium.
Brief but brutal Gaza conflict
In May 2021 an intense and deadly conflict lasting just eleven days erupted between Israeli and Palestinian forces. As on previous occasions, civilians paid the highest price. Airwars documented the human impact of this short but brutal conflict in both Gaza and Israel, working for the first time in three primary languages – Arabic, Hebrew and English.
The research found that Israeli strikes, continually impacting across the densely populated streets of Gaza, led to the likely deaths of between 151 and 192 civilians. Over a third of civilians killed in Gaza were children and in more than 70% of the allegations documented by Airwars, civilians – not militants – were the only documented victims. In Israel, ten civilians were directly killed by rockets fired by Hamas and Islamic Jihad from Gaza.
The report also documented civilian harm from Israeli strikes in Syria, which across eight years had led to the deaths of between 14 and 40 civilians. Comparatively this civilian harm estimate stands in stark contrast to the numbers of those killed in just eleven days. Gaza is one of the most densely populated places in the world, whilst Israeli strikes in Syria were conducted on military targets mostly in sparsely populated areas.
Airwars’ Senior Investigator Joe Dyke partnered with the Guardian on a piece interviewing the residents of a tower destroyed by Israel Defence Forces during the May 2021 conflict. Al-Jalaa Tower was home to dozens of civilians and a number of offices, including those of Associated Press and Al-Jazeera. All were given an hour’s notice to evacuate the tower and scramble together their possessions before seeing their homes destroyed in front of them. The investigation recently won an Amnesty Media Award.
Russian assault in Syria
Long before Russia’s assault on Ukraine in February 2022, Airwars had been tracking civilian harm caused by extensive Russian actions in Syria.
Whilst allegations of civilian harm fell to their lowest rate this year since 2015, after a 2020 ceasefire agreement between Russia and Turkey continued to hold, Putin’s forces continued to strike Idlib and other rebel-held areas of Syria with air and artillery strikes.
Approximately 48% of civilian harm allegations against Russia during 2021 occurred in Idlib, whilst 2% occurred in Hama, and 23% in Aleppo governorate. In total as many as 280 civilians were killed by Russian and/or Syrian regime air and artillery strikes.
This significant but comparatively lower civilian casualty count came alongside Russia’s escalation of military operations in preparation for Moscow’s invasion of Ukraine, which has subsequently led to mass civilian harm.
Explosive weapons
An overarching theme throughout Airwars’ work during the year, and a key focus for our advocacy outreach, was on restricting the use of explosive weapons in populated areas (EWIPA).
Whether in Syria, Iraq, Gaza or any of the other conflicts Airwars monitors, when explosive weapons are used in densely populated areas, the potential for civilian harm dramatically increases.
Throughout 2021, Airwars worked with international partners to support a strongly worded UN-backed international political declaration against the use of EWIPA. The final UN-backed conference debating this declaration will be held in summer 2022, with Airwars playing a key role advocating for change.
Visual article on Israeli attack in Gaza awarded best use of digital media
Airwars and The Guardian have won a prestigious Amnesty Media Award for their joint investigation into Israel’s striking of residential towers in Gaza.
The article, Countdown to the Airstrike, won in the Best Use of Digital Media category.
The article tells the story of the destruction a single tower in Gaza through their memories of the residents living there. The families were given only a few minutes to evacuate their belongings before Israel jets destroyed the building.
A screenshot of the story on The Guardian
Israel claimed that the tower was being used by the Islamist militant group Hamas, which controls Gaza, though residents strongly reject that claim.
Airwars was also nominated for its interactive mapping of civilian harm in Gaza during the conflict.
The full piece can be read here.
International gathering brings nearer a protocol on restricting explosive weapon use in urban areas.
States edged closer to a political declaration on the use of explosive weapons in populated areas on April 8th, after three days of crunch talks in Geneva.
More than 65 states descended on the Swiss city for key talks on the wording of a political declaration that advocates believe would save thousands of lives by restricting the use of wide area effect explosive weapons in populated areas (EWIPA). Detractors, such as the United States government, argue it would unfairly limit the freedom of their own military actions and have threatened not to sign.
While no final text was agreed upon Friday, all sides struck an optimistic tone at the end of the three-day meet – saying a deal was nearer than ever. Delegates will meet again for one day in two months before an adoption ceremony expected in the summer.
“There are clearly differences of opinion but we have seen a very positive, solution oriented approach,” the chairperson, Ambassador Michael Gaffey of Ireland, said. “We are not simply working on a formula of words in a political declaration – we want to make a real difference and impact on the ground and foster behavioural change.”
The talks were given additional urgency by the ongoing war in Ukraine, and Russia’s extensive use of explosive weapons on its cities. Moscow did not attend the talks.
Even the United States, widely viewed as one of the most hostile states to a declaration with teeth, struck a more positive tone than in previous meets. “There are still tough drafting issues and decisions ahead, and we have to get them right. The US delegation pledges our goodwill, to help to get to a positive outcome. We look forward to doing so.”
Since 2018, Ireland has chaired consultations on the use of explosive weapons in populated areas. In the sessions since, the need for such a declaration – which is not legally binding and so does not create new legal obligations – has only become clearer.
“The draft declaration text holds the potential to make a meaningful contribution to the protection of civilians, and negotiations over the past few days have overall been constructive,” Laura Boillot of INEW, a network of NGOs pushing for the protocol, told Airwars.
“But decisions will now need to be made if the final text is going to have humanitarian effect. Most importantly it needs to establish a presumption against the use of explosive weapons with wide area effects in towns, cities and other populated areas.”
It will be a failure to leave this room agreeing that simply restating existing laws will reduce civilian harm – a failure for all of us who came here with the intention to reduce that harm in the first place." @alma_osta in HI concluding remarks at #EWIPA negotiations today. pic.twitter.com/pTKpgfqWWU
— HI_Advocacy (@HI_Advocacy) April 8, 2022
Civil society groups and international agencies made a strong case for restricting EWIPA.
Three days of consultations
During three days of focused talks, several key fissures bubbled. While states in attendance – and civil society organisations – repeatedly emphasised the shared desire to produce a tangible and meaningful political declaration that could help save civilian lives on the ground, the practicalities of the process made clear that good intentions weren’t going to be enough.
On the first day of the informal consultations on April 6th, states made general remarks – affirming their support for the proceedings as well as their national positions – after an introductory statement from Ireland, the penholder.
In these general remarks, most states tended towards re-affirming the positions they had made clear in previous negotiations. On the hawkish side, the UK, US, Israel and Canada all emphasized that their positions as militarily active states meant that they would not sign a declaration in its current form, which included strong language about avoiding the use of explosive weapons in urban areas. Throughout the week, the delegates from these countries could often be seen meeting as a bloc outside of formal proceedings.
Many of the sticking points that emerged on the first day continued to dominate both the main floor and side conversations. The predominant line of argument was between those who argued that the declaration needed only to reaffirm the importance of international humanitarian law and provide further guidance about how to do so in this context; and those who asserted that this declaration needed to strengthen existing commitments and add new ones for states around the use of explosive weapons.
The second day of discussions took a more technical turn, with the majority of interventions focused on the wording of specific clauses and paragraphs of the text.
Clause 3.3, which attracted much attention in previous consultations, was once again hotly debated. It is one of the first clauses in Section B, the operative section – which lays out the actions that states have to comply with if they choose to sign onto the declaration.
In the current draft, Clause 3.3 says states must: “Ensure that our armed forces adopt and implement a range of policies and practices to avoid civilian harm, including by restricting or refraining from the use of explosive weapons with wide area effects in populated areas, when the effects may be expected to extend beyond a military objective.”
The bulk of the discussion around this clause was on the second sentence, as many states intervened on the use of “restricting or refraining,” with some suggesting it was strong enough while others lobbied instead for the use of “avoid”.
A split between the majority of civil society organisations and militarily-powerful states was apparent during these parts of the discussions, with NGOs and international agencies pushing for stronger language, rather than trying to place limits on what kinds of civilian harm would be protected under this new declaration.
Airwars’ incoming director and current head of research Emily Tripp also made an intervention – emphasising how crucial it was for states to actually track civilian harm.
Airwars’ incoming director Emily Tripp addresses a UN-backed conference on explosive weapons in Geneva on April 7th, 2022 (Image: Airwars)
At the end of day two INEW, one of the organisers, named nine states – Belgium, Canada, Denmark, Israel, the Republic of Korea, Sweden, Turkey, the United Kingdom and the United States – that it said had “worked to weaken declaration provisions.” The UK delegation, for example, agreed that tracking civilian harm was a ‘moral obligation,’ but then highlighted ways in which it claimed this was not feasible – arguing that live hostilities made it near impossible to monitor casualties properly.
But INEW also said that there had been a “shift in the collective tone set by states since the last round of negotiations, with more governments explicitly committed to strengthening the protection of civilians through the declaration.”
The statement said this was likely as a response to the bombing of Ukrainian towns and cities, and the Ukraine crisis loomed large over the conflict. Not only did the majority of states open their remarks with condemnation of the Russian aggression in Ukraine, many also emphasised the importance of a meaningful political declaration with specific reference to Ukrainian cities and towns such as Mariupol, Bucha and Khrarkiv.
There was also an emphasis on the value of protecting civilian objects and infrastructure, such as schools and hospitals, with states such as Mexico and the delegate for the Holy See (which holds observer state) urging specific language around the need to protect hospitals, blood transfusion centres, and environmental and religious sites.
Speaking at the end of the latest talks, Ambassador Gaffey said Ireland and organisers would review the submissions from all parties before a month or two of further work on the text. He said states and NGOs would then hold a final one-day consultation in a couple of months, before a political adoption ceremony where states would declare their support for the text.
As Alma Taslidžan Al-Osta, of Humanity and Inclusion, noted in her own concluding remarks to delegates: “Eleven years in Syria, seven years in Yemen and over a month in Ukraine have taught us that explosive weapons with wide area effects should not be used in towns, cities and populated areas. The status quo is no longer an option.”
Civilians increasingly bear the brunt of modern conflicts. Addressing the devastating harm to civilians from Explosive Weapons in Populated Areas is a priority for 🇮🇪. We welcome states, international organisations and civil society to consultations in Geneva this week #EWIPA pic.twitter.com/pAyglwZO9D
— Disarmament IRELAND (@DisarmamentIRL) April 6, 2022
Ireland chaired Geneva talks on restricting urban use of explosive weapons
Crunch talks in Geneva aim to hammer out protocol on explosive weapons in urban areas
The shadow of the Ukraine conflict loomed large over the first day of the informal UN-backed consultations on a political declaration on restricting the use of wide area effect explosive weapons in populated areas (EWIPA), currently underway in Geneva.
Delegates from more than 65 nations have gathered to fine tune the language of the political declaration, along with more than 15 civil society organisations including Airwars. The chairperson, Michael Gaffey of Ireland, opened the proceedings by calling for a minute of silence for Ukraine.
Nujeen Mustafa, who had fled the war in Aleppo, then powerfully testified via a video message, saying, “throughout history, diplomats have discussed world problems while sitting at a table with a nice coffee. People trapped in a conflict zone cannot do that. Today, you have the possibility to change a terrible situation and protect civilians.”
Nujeen Mustafa, a Syrian who fled Aleppo after it was largely destroyed by explosive weapons, addresses delegates:“While you’ve been negotiating whether a declaration should be made, 11,076 people have fallen victim to these weapons" she sayshttps://t.co/DI9vYhD6nq
— Airwars (@airwars) April 6, 2022
While there are two days of discussion left before proceedings close on Friday evening, many of the most pressing issues arose in proceedings on Wednesday – particularly as states laid out their own positions during opening remarks. Here are five key themes from the first day of EWIPA negotiations.
1. The conflict in Ukraine adds a sense of urgency
The first statement was made by the Ukrainian delegate, who noted that “our cities and towns have been turned into dead ash because of the use of these explosive weapons” – highlighting a new sense of urgency and relevance which the negotiations have taken on.
Every delegate who spoke made reference to the Ukraine conflict, with many emphasising that the violent and horrific violence against Ukrainian civilians must move states to act more effectively. The French delegate noted that Russia did not attend the proceedings, while the Japanese delegation emphasised the importance of documenting civilian harm in Ukraine.
Many other states called on Russia to cease its aggression and indiscriminate bombing of civilians and it was noted multiple times that Russia’s campaign has targeted and destroyed civilian neighbourhoods using wide area effect explosive weapons – referring to the scenes of destruction in Kherson, Mariupol, and Kharkiv.
2. The gap between ‘IHL is enough’ and ‘IHL does not go far enough’
Broadly the delegates and countries fall into two groups – those that believe international humanitarian law (IHL) is enough to protect civilians under attack in urban areas – and those that argue more is needed to protect civilians.
States such as the USA, UK, France and Israel argued that any political declaration could not introduce new legal requirements (which it cannot) and that the requirements currently set out under IHL should be sufficient protection for civilians. Currently, these frameworks emphasise for example that deliberately attacking civilians and civilian infrastructure constitutes a violation of IHL – and that any military actions must be both proportionate, and distinguish between civilians and combatants.
Those backing strong wording to the political declaration text – from Ireland to the ICRC – insist that adherence to IHL alone is not doing enough to protect civilians during much urban fighting.
The US nevertheless called on those states gathered not to produce an “unrealistic impression” that civilians would not be harmed in conflict, while emphasising that explosive weapons are “considered a legitimate and lawful means of warfare when used in accordance with IHL.”
But other states, as well as civil society organisations such as Human Rights Watch, emphasised that any resolution which merely restated the value of IHL – and how states must abide by it – would effectively be useless, as it would be an iteration of what states have already committed to.
States such as Finland and Sweden remarked that there are gaps within IHL around EWIPA , and mere compliance with IHL is not enough to protect civilians. This has been an ongoing fissure during previous consultations, and continues to be a major fault line.
3. Reverberating effects
The particularities of the language used in the eventual political declaration are at the heart of the ongoing consultations in Geneva – with discussions about whether to “avoid” or “restrict” the use of explosive weapons in populated areas already a key sticking point.
An additional area of tension appears to the so-called “reverberating effects” of EWIPA, which are essentially the long-term effects.
An example of a reverberating effect would be the destruction of a bridge. If destroyed, it has the immediate effect of removing a crucial piece of civilian infrastructure. But even after the conflict finishes the destruction could also mean that people can’t travel across a certain river, making it harder to access other kinds of civilian infrastructure such as hospitals or schools.
These long-term impacts were the subject of much discussion on Wednesday – with some states, such as the US, Israel, and the UK all noting that ‘reverberating effects’ is neither a legal term nor – they claimed – a widely accepted term with a clear definition. The US also said it would not accept a ‘novel’ term such as reverberating effects in the eventual political declaration.
However, civil society organisations such as PAX and observer states such as the Vatican suggested that it would be difficult to meaningfully understand the full implications of how civilian populations were impacted without incorporating ‘reverberating’ effects.
4. Focus on the humanitarian impacts
The Holy See opened its own remarks by noting that it believes conventional weapons should be named “weapons of mass displacement,” a nod to the ongoing long term effects that explosive weapons can have. The Danish Refugee Council also noted that the use of EWIPA can contribute to displacement, and in time, continuously produce forms of renewed displacement.
Some other states such as Uruguay emphasised the need to collect and monitor the impacts of EWIPA on specific groups – such as those with disabilities, or those who face discrimination because of their gender. Organisations such as CIVIC, PAX and Humanity and Inclusion also spoke about the psychological and mental effects of the use of explosive weapons, notably the need for a survivor-centric approach to any kind of political declaration.
5. The impact of non-state actors
While the political declaration is primarily a matter between states, the UK, Israel, the US and others asked that the considerations around EWIPA must also extend to non-state actors, such as armed groups, in the interest of maintaining what they termed a balanced account of how explosive weapons are actually used in populated areas.
The US noted for example that “the declaration has to make it clear that all belligerents, including non-state armed groups, must take steps to address the harms to civilians and civilian objects.” The Turkish delegation argued that asking non-state actors to really consider these impacts would also mean they would be considered as legitimate parties to an international armed conflict – which they are currently, for the most part, not.
The declaration has to make it clear that all belligerents, including non state armed groups, must take steps to address the harms to civilians and civilian objects,” says the USA, intervening for the second time today. pic.twitter.com/cNBYvzncqN
— Airwars (@airwars) April 6, 2022
Speaking at key Geneva talks, SNP's defence spokesperson calls on nations to back strong EWIPA protocol
Stewart McDonald MP, the defence spokesperson for Scotland’s ruling Scottish National Party (SNP), called on Wednesday for the United States and United Kingdom to join those nations backing restrictions on the use of explosive weapons in urban environments during key talks in Geneva.
On April 4th the SNP became the largest British party – and one of the largest in the world – to lend its support to restricting the use of explosive weapons in urban areas (EWIPA).
The policy – part of a wider SNP Protection of Civilians paper expected soon – was announced to coincide with crunch talks in Geneva, where dozens of countries are meeting to hammer out the wording of a protocol, or political declaration, on EWIPA. While the proposals are supported by the United Nations and many other nations, both the United States and United Kingdom are currently expected to oppose the protocol, while Russia is not attending the talks.
“It is unlikely that the United States or Russia are going to be signatories to it and that is deeply unfortunate – in fact it is worse than unfortunate,” Stewart McDonald MP told Airwars. “I am convinced that deeper cooperation internationally is what we need right now.”
During three days of talks, representatives from more than 65 nations are meeting in Geneva to discuss the potential final language of the political declaration. In Wednesday’s opening session, the US again said it had major reservations about restrictions on explosive weapons use.
The US and other states critical of the protocol argued that international human law is enough to limit civilian harm, but advocates say that when used in cities weapons designed for the open battlefield will always disproportionately harm civilians.
McDonald added that he was “optimistic” rather than confident that a strong text could still be agreed. But he raised concerns that the wording could be watered down by obstructive nations, including the United Kingdom, making it effectively meaningless.
“We will see what comes at the end of it, but anything that is not robust, that doesn’t have broad, multilateral buy-in to it, might make some people feel good – but I am not sure I would call that a success.”
🇺🇳 My remarks at today’s session at @UNGeneva on the #EWIPA negotiations, being led by 🇮🇪 @dfatirl. It was a pleasure to speak alongside fellow parliamentarians from Belgium 🇧🇪 and France 🇫🇷. The growing international consensus needs to coalesce around robust civilian protections pic.twitter.com/PWpUTSb8zz
— Stewart McDonald (@StewartMcDonald) April 6, 2022
McDonald said the new SNP declaration was a significant moment for both his party and the United Kingdom. The text declares that there “must be a presumption against the use of wide-impact explosives in conflicts that take place in populated and urban territories. SNP fully supports the ongoing UN-backed process to develop a political declaration addressing the use of explosive weapons in populated areas.”
The announcement comes ahead of a full approach the party intends to announce later this month outlining how the SNP, and potentially a future independent Scotland, would seek to protect civilians in conflicts.
“I believe my party should think like a state and act like a state – so if Scotland were independent, how would it approach these issues? That’s why we have taken the time to develop a policy around protection of civilians to show people where we think people would go.”
“But importantly, in the here and now what the UK government should be doing.”
While the SNP’s defence spokesperson said that Russia’s invasion of Ukraine – which has seen thousands of civilians killed while trapped in cities – had focussed attention on the scourge of explosive weapons use, McDonald also highlighted similar civilian suffering in Syria, Iraq, Yemen and elsewhere. Research by Action On Armed Violence indicates that around 90 percent of those killed and injured by explosive weapons in populated areas are civilians.
“Ukraine has gathered the public and political momentum now [and] I think that does mean correctly that these negotiations take on a particular urgency to succeed and deliver something meaningful.”
“How do you scroll through social media right now, and not want something serious to happen?”
The political declaration talks are continuing until April 8th. Airwars’s social media coverage of the first day can be viewed here.
Full text of SNP policy extract: Explosive Weapons in Populated Areas
When explosive weapons are used in populated areas – where conflicts increasingly take place – studies suggest that more than 90% of those killed and injured are civilians. Vital facilities such as sanitation systems and hospitals are disproportionately destroyed in attacks using these weapons, exacerbating risks to civilians who become further exposed to deadly diseases and further robbed of medical assistance. There must be a presumption against the use of wide-impact explosives in conflicts that take place in populated and urban territories.
SNP fully supports the ongoing UN-backed process to develop a political declaration addressing the use of explosive weapons in populated areas. An independent Scotland would look to sign on to this declaration. Additionally, Scotland should ratify the 2008 Convention on Cluster Munitions as well as the 1997 Anti-Personnel Landmines Convention.
Crucial UN-brokered talks begin on restricting heavy explosive weapon use in populated areas
State delegates from around the world will meet this week in Geneva for UN-backed crunch talks, working towards a political declaration on restricting the use of wide area effect explosive weapons in urban conflict. If successful, the move could help save thousands of civilian lives.
Representatives from more than 60 countries will meet from April 6th-8th in the Swiss city of Geneva to try and hammer out the wording of a protocol, or political declaration, on restricting the use of wide area effect explosive weapons in populated areas (EWIPA).
As wars have increasingly moved from open battlefields to urban environments, weapons designed for the former are being deployed in heavily populated areas – sharply increasing the risks of harm to civilians and civilian infrastructure.
UN and civil society reports have repeatedly found that civilians and civilian infrastructure are at most risk when heavy explosive weapons are used in populated areas. This has been clearly demonstrated in recent weeks in Ukraine as Russian forces have pounded civilian neighbourhoods with devastating results, but has also been documented in other recent conflicts across the globe.
Research by Action On Armed Violence indicates for example that around 90 percent of those killed and injured by explosive weapons in populated areas are civilians.
“Ukraine puts a spotlight on the devastating consequences civilians face when towns and cities are bombed. But this is a pattern of harm that we see elsewhere too: Ethiopia, Gaza, Iraq, Yemen, and Syria are all recent examples,” said Laura Boillot, coordinator for the International Network on Explosive Weapons, which is leading civil society efforts to restrict EWIPA use.
To highlight the EWIPA talks, the campaigning group Humanity & Inclusion has installed a tank made of balloons outside the United Nations in Geneva (Credit: Megan Karlshoej-Pedersen/Airwars)
“This week, states have an opportunity to reduce civilian harm and agree a new international declaration that commits states to avoid the use in populated areas of explosive weapons with wide area effects.”
In 2019, Ireland convened the first EWIPA negotiations, inviting delegates from every country to join and shape a resolution to change how explosive weapons are used in populated areas.
In the years since, delegates have continued to gather to discuss the text of the declaration – which will be finalised and ratified by states this summer.
While not a United Nations process, the EWIPA proceedings are backed heavily by the UN; and Secretary General Antonio Guterres has repeatedly called for countries to adopt a strong protocol.
When explosive weapons are used in populated areas, 90% of the casualties are civilians, causing devastating suffering.
I again call on countries to avoid using explosive weapons in populated areas. https://t.co/OS4OgqJ771
— António Guterres (@antonioguterres) March 30, 2022
US, UK, France in focus
During three days of talks in Geneva, representatives from attending countries will pore over the draft resolution and try to agree on key sections of text.
Much of the focus will likely be on winning the support of those states which have previously attempted to water down the declaration’s language, including the United States, the United Kingdom and France. While some states argue that abiding by international humanitarian law (IHL) is enough, others like Britain also claim that limiting explosive weapon use in cities “would reduce the UK’s ability to operate legitimately and responsibly.”
Critics say that adherence to IHL alone is not sufficient to protect civilians during attacks on cities – a point recently supported by a major Pentagon-published study into the ferocious 2017 Battle of Raqqa, which noted that the US-led Coalition caused “significant civilian harm despite a deeply ingrained commitment to the law of war.”
Efforts by the US, UK and others to water down the political declaration would make it effectively useless critics warn – and crucially, would not lead to changes in the way that states actually approach the use of explosive weapons in cities.
Given the horrors of urban civilian harm in Ukraine, a very disappointing answer from UK government on whether it will commit to restrictions on explosive weapons use in cities, at upcoming @UN talks in Geneva. (Thanks to @MargaretFerrier for question.) https://t.co/BHWDagQD1D pic.twitter.com/LmK7mgStKv
— Airwars (@airwars) March 17, 2022
Detailed negotiations
The draft resolution being discussed at Geneva consists of two parts – a preamble, which lays out the framework and overall considerations; and the operative section, which effectively compels states to act. For example, the value of tracking civilian casualties in real-time are currently mentioned in the preamble, but aren’t in the operative section – though some states are pushing for it to be moved there.
Broadly speaking, those attending the political declaration talks can be split into two camps: those states that argue the resolution should use weaker language; and those nations – backed by the UN – arguing that the declaration should be as strong as possible.
Other key states, including Russia and China, are not expected to attend this round of talks.
Among the strongest advocates for an effective political declaration is Ireland, which has led the process. UN Secretary-General Antonio Gutteres has also called for “strong” wording. “The Secretary-General supports the development of a political declaration, as well as appropriate limitations, common standards and operational policies in conformity with, and further to existing requirements under, international humanitarian law relating to the use of explosive weapons in populated areas,” he said in a recent statement.
Some countries, such as Belgium, have already passed their own parliamentary resolutions indicating that they will be signing the declaration, although it is still unclear how this would be implemented in practice.
While these negotiations were originally planned to be the final in a series of discussions, there may still be a further round ahead of final ratification in the summer. In the meantime, supporters of controls on explosive weapon use in cities believe that Russia’s extensive use of indiscriminate large weapons on Ukrainian cities – and the horrific civilian toll associated with such attacks – may help sway wavering countries.
Armed conflicts in urban areas are increasingly fought with weapons that are not designed or adapted to be used in populated areas.
As a result, the effects of these weapons go well beyond their targets and have devastating consequences for civilians. pic.twitter.com/UUS2YMWW0x
— CIVIC (@CivCenter) April 1, 2022
In news widely welcomed by team, Emily Tripp to take over as organisation's second leader this summer.
Emily Tripp will be the next Director of Airwars, the organisation’s Executive Board announced today, and will succeed the present head of the organisation Chris Woods in the summer.
Emily is presently Airwars’ Research Manager, where she has strongly led on recent projects including the team’s monitoring of the conflict between Israel and Gaza in 2021 – which was recently shortlisted for an Amnesty Media Award.
Emily has previously worked in the humanitarian sector, managing monitoring and evaluation departments in Syria and assessment teams in Libya. She brings to the Director’s role technical expertise in data collection in volatile conflict environments, as well as leadership experience overseeing large teams across different countries and regions.
“We are beyond thrilled to know that Emily will lead Airwars into its next iteration, in which civilian harm monitoring, archiving of open-source data, and research and advocacy on behalf of affected communities will continue to form the heart of our work,” the Board noted in a statement. “Emily’s talent, strategic vision and collaborative approach make her the ideal leader to build on the outstanding work done by Chris and the rest of the Airwars team.”
Emily Tripp will be the organisation’s second Director, succeeding Chris Woods who co-founded Airwars in 2014. He saw the organisation through a strong growth phase in which civilian casualty monitoring was introduced across multiple conflict situations in Iraq, Syria, Libya, Somalia, Yemen, and the Gaza Strip. His work at Airwars also helped set the bar for accountability for military action in air-dominated conflicts around the world.
“Chris has been an invaluable asset to Airwars since its founding in 2014. He has been the driving force in building a unique organisation dedicated to the monitoring of civilian harm that has become recognised globally as the gold standard for accountability and transparency for belligerents in conflicts,” read a statement from Airwars’ Executive Board.
In further news, Dmytro Chupryna – Airwars’ Deputy Director since 2018 – decided to step down at the end of March. During his time with Airwars, Dmytro led on organisational, fundraising, and civil advocacy issues – and has been a critical contributor to the organisation’s ongoing success.
“We are all incredibly sad to see Dmytro move on – though his positive legacy will be with us for many years to come,” noted outgoing Director Chris Woods. “We wish him every success in his future career.”
Today was my last day at @airwars. I'd like to thank all the amazing Airwars team and our large POC family for unbelievable four years. It was an absolute honour and pleasure to working with all of you 💙💛 and thanks for wonderful flowers and gifts ☺️👐 will miss you a LOT! pic.twitter.com/O0SihF1DZX
— Dmytro Chupryna (@ChuprynaDmytro) March 25, 2022
The longstanding Chair of Airwars Elizabeth Minor has stepped down due to ill health.
Elizabeth Minor, the longstanding voluntary Chair of Airwars, has sadly stepped down due to ill health, the organisation’s Board has announced.
Since joining the Airwars Board in summer 2016, Elizabeth has been a critical driver of the organisation’s many successes.
A leading conflict casualty recording expert, Elizabeth was a key contributor to Every Casualty Counts’ world first Standards for Casualty Recording; is a co-recipient of the 2017 Nobel Peace Prize for her work with ICAN in helping galvanize successful negotiations of a global treaty prohibiting nuclear weapons; and is a key adviser with Article 36, the international NGO focused on reducing harm from weapons.
Elizabeth Minor: stepping down due to ill health
Among many accomplishments during her time chairing Airwars’ volunteer Board, Elizabeth led on the development of the organisation’s secondary trauma reduction policy in partnership with the Dart Centre for Journalism and Trauma; and was a champion throughout of the highest ethical and research standards. She also chaired the Airwars Advisory Board.
“I’m very proud to have been able to contribute to Airwars’ Boards as the organisation has developed from a very small startup to the established, professional and widely respected organisation it is today,” Elizabeth said this week.
“Of the work we have done together, I’m particularly proud of our establishing procedures for trauma risk management within the organisation – which no similar NGO had comparable policies on at the time we did this work.
“I’m looking forward to seeing where Airwars goes next and collaborating in other capacities, and wish the team and Boards all the best. It has been wonderful to work with such an excellent group of people.”
Speaking about Elizabeth’s departure, Airwars’ outgoing Director Chris Woods described her as “a wonderful, passionate and expert Chair who along with her volunteer colleagues has made an immeasurable contribution to our successes as an organisation. Elizabeth will be very much missed, and we wish her the very best.”
New Board member announced
A new Chair is expected to be appointed at Airwars’ next Annual General Meeting in the Spring. In the meantime, Aditi Gupta has been seconded to the Board with the warm support of staff, volunteers and other Board members.
Director for the All-Party Parliamentary Group on Drones and Modern Conflict, Aditi is also Deputy Director for the UK Chapter of Women of Color Advancing Peace and Security. She previously managed the Freedom Online Coalition Secretariat, through her role at Global Partners Digital where she worked on strengthening civil society advocacy in cyber policy processes.
“I’ve closely followed Airwars’ vital work since their inception, and I’m so proud to work with them officially as a member of the Board. Over the years, the team at Airwars has built an unignorable evidence base of allegations, putting the experience of and impact borne by civilians in conflict firmly at the door of those who need to take accountability,” Aditi said this week.
“I wholeheartedly support this important work, and hope my experience in parliamentary engagement, organisational management, and efforts working on intersectional justice and equality issues will bolster their strength further.”
Aditi Gupta has now joined the Airwars Board
Update on Director recruitment
In a further update this week, the Board said that it has unfortunately not yet been successful in its efforts to appoint a successor to Chris Woods, the founding Director of Airwars who announced he would be stepping down after more than seven years in the role.
Brexit and COVID between them have made for a very challenging UK jobs market at present, and the Board says it is determined to ensure the best possible appointment as Director to take the organisation forward. In the meantime the Board has asked Chris Woods to stay on temporarily as Director.
“The Board is immensely grateful to Chris for agreeing to delay his departure for a few months while we complete our process to find the right leader to build on his incredible work, and ensure a smooth transition once they are appointed,” notes Airwars Treasurer James Hirst.
Further updates on the recruitment process are expected in the weeks ahead.
Airwars has found that 10 times more civilians were killed in 11 days of Israel’s bombing of Gaza than in the entirety of its 8-year campaign in Syria
This article was originally published by Newlines on December 9th 2021 and written by Airwars’ Investigations Team.
On Jan. 13, 2021, the Israeli military launched some of its most intensive strikes to date in Syria. Over several hours, perhaps two dozen sites of Iranian-linked armed groups were hit over a vast territory in the Deir ez-Zor region near the Iraqi border. At least 57 militants were reportedly killed. Local communities did not report a single civilian casualty.
Four months later, the might of the Israeli military targeted a very different location.
On the night of May 15, a series of airstrikes hit the Al-Rimal neighborhood of central Gaza City. At least 44 civilians reportedly died. Multiple families were nearly wiped out after taking shelter in a neighborhood previously thought to be safe. Some Hamas militants may also have been killed in underground tunnels, the announced target of the strikes by the Israel Defense Forces (IDF), though this remains unclear.
The death tolls on those nights were not an anomaly — they form part of a clear trend. The Israeli military has fought two largely aerial campaigns in recent years. One is a yearslong campaign to prevent the Iranian military and its allies from entrenchment in Syria, the other a brief but fierce war with Hamas and other militant groups in Gaza in May. The effect on civilians could hardly be more stark.
New research by Airwars has found that up to 10 times more civilians were killed in 11 days of bombing in Gaza than in the entirety of Israel’s eight-year campaign in Syria.
In Syria, several hundred secretive Israeli strikes since 2013 have likely killed as many as 40 civilians. Rough tallies suggest hundreds — and likely thousands — of Iranian and Syrian military personnel and militants of other nations were killed in these strikes. Civilian casualties from the Israeli campaign appear to be dramatically lower than those resulting from other foreign powers operating in Syria — including Russia, Turkey and the U.S.-led coalition.
In Gaza the civilian-militant ratio is reversed. Between May 10 and 21, from 151 to 192 civilians were likely killed by Israeli airstrikes, according to a comprehensive review of local community reporting by Airwars. While this research didn’t estimate the number of militants killed, Israeli rights group B’Tselem put it at 90.
The Israeli actions in Gaza and Syria are usually thought of separately — with comparisons between the two rare. But how did a military that runs such a careful campaign in one theater end up killing so many civilians in just a few days in another? Our research pointed to three main reasons for the discrepancies.
The first is the type of targets chosen by the IDF in the two contexts. Israel’s targeting system bears many similarities to that of its closest ally, the United States. In fact, Israeli military lawyers pioneered the legal justifications for the targeted assassinations that later became a hallmark of the war on terror.
Until 2000, Israel legally considered Palestinian opposition a matter of law enforcement, said Daniel Reisner, then head of the Israeli military’s International Law Department. But following the outbreak of the second Palestinian uprising, or intifada, the Israeli military effectively invented a “hybrid” model to apply the laws of armed conflict — normally meant to apply only between states at war — to the West Bank and Gaza.
Craig Jones, a lecturer at Newcastle University and author of a recent book on Israeli and U.S. military lawyers, said by expanding the concept of “direct participation in hostilities,” Israel effectively invented a new category of potential target between civilian and combatant — allowing it to justify a widespread campaign of targeted assassinations.
“Essentially, once a Palestinian ‘participates’ by the broad Israeli standards, he or she cannot put down arms and remains targetable even when resting at home,” Jones said.
Reisner recalled that U.S. officials initially criticized the policy but after 9/11 “started calling for advice.” Later U.S. official justifications for drone strikes included lines lifted almost directly from Israeli policy, he said.
This legal justification allowed for more freedom in targeting Palestinian militants in their homes. While potential civilian harm still needed to be considered and precautions taken, it was accepted by the Israeli system that hitting a militant at home was potentially justified.
When the Gaza conflict started on May 10, the IDF would have had dozens of targets that had been preapproved — meaning they had already been through legal and military review.
“The IDF would have taken out of its drawers plans that were pre-prepared and reviewed legally,” said Liron Libman, former head of the International Law Department at the IDF. “But then every plan is just the basis for an order. To turn it into an operational order, you still need to assess the information again.”
It seems likely that many of those preapproved targets were the homes of militants.
Airwars tracked 17 locally reported incidents in which militants were explicitly targeted in residential buildings and civilians were killed or injured. Most took place in the first four days of the conflict, suggesting that they were in a preapproved target bank.
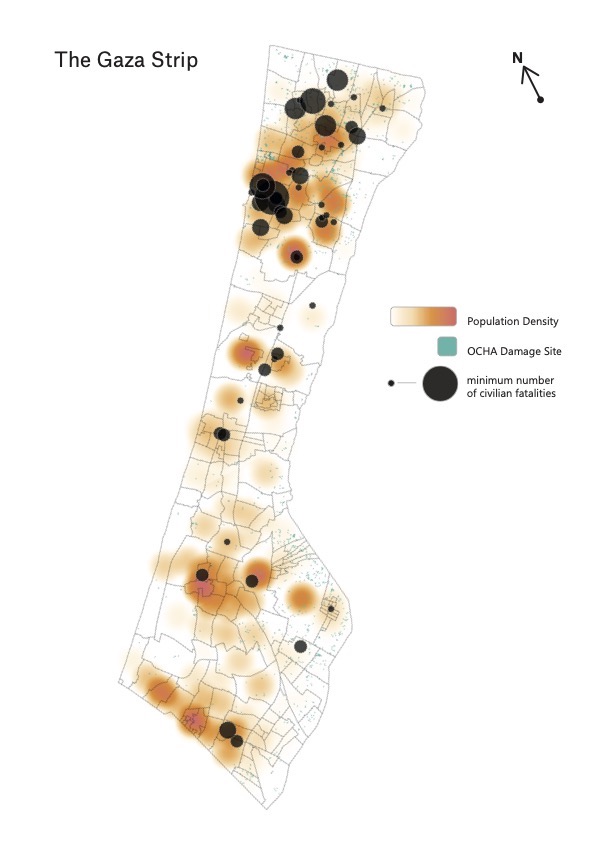
Airwars mapping of all civilian harm and strike locations (in light green according to UN data), mapped onto population density in the Strip
In those 17 incidents, local reports found that from nine to 11 militants were killed but also from 27 to 33 civilians, with more than 100 injured.
In one incident on May 13, four civilians were killed and 15 more, including seven children, were injured. The target was a three-story house in the Al Jeniya neighborhood, where four families lived. One of the dead, Raed Ibrahim al-Rantisi, was identified by the al-Qassam Brigades as one of their fighters. The family had gathered for Eid dinner.
In Syria, such incidents are rare, though not unheard of — such as when a Palestinian official and his family were killed in a strike in central Damascus in November 2019. But in general, strikes in Syria seem to target militants at exclusively military targets such as weapons warehouses close to land borders. Some of the civilian harm associated with Israeli strikes may even have been a result of Syrian air defense missiles missing their targets and hitting civilian homes.
The IDF’s practice of striking homes in Gaza also contributed to the high percentage of children killed, with more than one-third of all civilians killed there reported to be children. In Syria the figure is around 10%.
Likewise, when Israeli forces killed a civilian in Syria, more than 70% of the time they also harmed a militant, whereas in Gaza that ratio was in the 30% range.
“In Syria we bomb military targets, while in Gaza we strike civilian areas, so we end up bombing families,” said Yehuda Shaul, of the Israeli human rights organization Breaking the Silence, which is made up of former IDF military personnel.
Population density
A second key factor that helps explain these very different outcomes for civilians in Syria and Gaza is population density. Gaza is among the most heavily populated territories in the world, which dramatically increases the likelihood of civilian casualties and damage to civilian infrastructure for every strike carried out.
We mapped every reported civilian harm incident in Gaza and every recorded strike location tracked by the United Nations, against population density.
Even within Gaza, civilian casualty incidents were clustered around areas of relatively high population density, such as in Gaza City to the north.
“Unlike in past wars, in May the Israeli military started its bombardment by hitting heavily populated areas and high-rise buildings,” said Yamen Al Madhoun, fieldwork director at the Gaza-based Palestinian rights organization Al Mezan. “Normally, people flee the perimeter areas where Israeli troops are stationed [and go] to schools and relatives’ homes in cities. But if civilian areas are the primary target, where can people go?”
Population density may also have provided some victims with a false sense of security. On May 12, airstrikes on the Tel al-Hawa neighborhood apparently targeting Hamas’ military wing destroyed two residential buildings. Reema Saad, who was four months pregnant, was killed alongside her two children and husband. The family had decided to stay in their apartment because they believed the densely populated neighborhood would be immune from strikes, Reema’s mother Samia told Middle East Eye.
Samir Zaqout, Al Mezan’s deputy director, said civilians had no idea how best to stay safe. “Fear, panic and confusion spread among the population. There were no taxis or transportation, so people were carrying their possessions and sometimes other family members while fleeing on foot.”
The Israeli military frequently notes that Hamas has placed military infrastructure in civilian neighborhoods in Gaza City, pointing to alleged tunnel networks as violations of the laws of war. Israeli officials also argue many of the more than 4,000 rockets fired by Hamas and Islamic Jihad from Gaza came from heavily populated neighborhoods.
But critics point out that hitting such neighborhoods overwhelmingly leads to civilian harm.
“Israeli authorities have shown an utter disregard for civilian life,” Omar Shakir of Human Rights Watch said. “They have a quite loose definition of what is a ‘military target,’ and they have consistently bombed in heavily populated neighborhoods without considering the civilian ramifications.”
“The rules and principles found in customary international humanitarian law to protect civilians should be followed,” Zaqout said. “Israel’s high-level military technology enables its forces to do so — to ensure the lawfulness of a target prior to attack. If circumstances are unclear, the Israeli military should presume people and objects normally dedicated to civilian purposes to be civilian.”
Even in Syria, the trend is noticeable. While the scale of civilian harm from IDF strikes is far lower than in Gaza, it is still overwhelmingly located in heavily populated areas, particularly the capital of Damascus — where around 45% of the estimated civilian harm occurred. In rural Deir ez-Zor Israel has carried out extensive strikes for more than five years, killing hundreds of militants and Iranian and Syrian military personnel along the way, without a single credible local allegation of civilian harm.
By contrast, both the U.S.-led coalition and Russian forces have caused often devastating numbers of civilian casualties during their own campaigns in Syria — primarily driven by extensive strikes on urban centers.
Such concerns chime with widespread calls for limits on the use of explosive weapons in populated areas. A U.N.-backed campaign now involving more than 120 nations — to forge a political statement that could help limit explosive weapons use in urban areas — is being led by Ireland, though so far no major military powers have fully thrown their weight behind it.
Rules of Engagement
A third possible factor helping explain why outcomes for civilians differ so radically between Israeli campaigns is one that is harder to prove — that the Israeli military has different, and more expansive, rules of engagement (RoE) for strikes in Gaza compared with Syria. Such RoEs govern when militaries are allowed to use force and, in the event that a strike is likely to kill civilians, determine how many casualties are deemed “acceptable.”
There are no internationally agreed-upon rules of how many civilians can be killed in a strike — international law requires only that it be “proportional” to the military advantage gained. At one point during the presidency of Barack Obama, U.S. generals in Iraq were allowed to carry out strikes they expected might kill up to 10 civilians, whereas the same figure in Afghanistan was at times set at just one, given the political sensitivities of civilian harm.
Multiple sources said the Israeli military does not internally quantify these “acceptable” tolls quite so explicitly, preferring instead to be “very context specific,” as Libman, now research fellow at the Israel Democracy Institute, said. The country has never released its RoEs for Syria or Gaza, and it is unlikely to do so.
A recent study found that Israeli military officers in general were significantly more conservative in their view of acceptable levels of civilian harm in discussions on proportionality as compared with their U.S. counterparts. The study, by universities in Israel, the U.S. and the U.K., found that in an imagined case of targeting an enemy headquarters, the median number of civilian deaths that U.S. officers were willing to tolerate in order to achieve military gains was 175, while Israeli officers were willing to accept 30 such casualties.
The IDF also likes to highlight its policy of warning civilians in Gaza before some airstrikes, a practice not widely adopted by other military actors. Yet these are the exception rather than the rule — in the 136 civilian harm incidents Airwars researchers tracked, the vast majority of targets had reportedly received no warnings.
According to Breaking the Silence, when there is imminent threat to populations, Israeli militaries are willing to carry out strikes that threaten civilian lives. “When there is even the slightest threat to Israeli lives, concern for Palestinian civilians all but goes out the window,” Shaul said.
Reisner didn’t dispute that the calculations were different in Gaza. “If I see an enemy about to fire a rocket at an Israeli city, the proportionality calculation would be different than if I saw the same individual at home knowing he is planning an attack in three days,” he said.
“I can legitimately kill many more civilians — it is a horrible sentence, but [it is the reality].”
Hamas and Islamic Jihad also posed a far more imminent threat than Iranian groups in Syria, said Amos Guiora, a professor at S.J. Quinney College of Law at the University of Utah and another former senior Israeli military lawyer. “With the Iranians you can afford to wait for the right time,” he said.
Politics may also play into it. Guiora said that the potential for a political fallout from a strike in Syria could also encourage caution. Israel has long had de facto control over the Palestinian territories but open involvement in Syria could risk a backlash at a time when Israel has secured landmark deals with Arab states including the United Arab Emirates.
“An unacceptable number of civilian deaths opens the door to blowback and bounce back, in the court of international opinion,” he said.
“Maybe from a geopolitical perspective, extra caution is necessary in Syria.”
Population density is greatest driver of civilian casualties from strikes in Gaza, Israel and Syria, new study shows.
In just eleven days in May 2021, Israeli air and artillery strikes on Gaza killed up to 10 times more civilians than the country’s eight-year bombing campaign against Iranian-linked forces in Syria, new Airwars research has found. The study raises critical concerns about the use of explosive weapons in populated areas.
The report – ‘Why did they bomb us?’ Urban civilian harm in Gaza, Syria and Israel from explosive weapons use’ – comprehensively documents the civilian toll of recent Israeli actions in Gaza and Syria, as well as from Palestinian rocket fire into Israel during May. Published jointly in Arabic, Hebrew and English, the 16,000 word report employs Airwars’ standard methodology to examine how, when, and where civilians are killed in urban conflicts.
The report chronicles civilian casualties from two very different military campaigns by the Israel Defense Forces (IDF).
Among the report’s key findings are:
-
Across the three conflict areas, both the targeting approach and the population density of those areas bombed were critical drivers of civilian harm, leading to profoundly different outcomes for civilians.
In Gaza between 151 and 192 civilians were likely killed as a result of IDF actions in May 2021, mostly in densely populated areas. At least a third of those killed were children. Between 15 and 20 civilian deaths in Gaza were additionally likely to have resulted from Palestinian misfires.
10 civilians were directly killed in Israel in May 2021 resulting from Palestinian militant actions – with most casualties occurring when rockets penetrated Israel’s ‘Iron Dome’ defence system and reached cities and towns.
In Syria, an extensive IDF air campaign since 2013 has had a far smaller impact on civilians. Israeli strikes have likely killed at least 14 and up to 40 Syrian civilians, with attacks mostly focused on exclusively military targets, away from population centres.
Airwars has produced an interactive map showing its findings for Gaza, which can be viewed here. The map allows users to navigate through 128 individual assessments of civilian harm in Gaza, and provides a lasting testimony to the civilian victims of the conflict.
Israel’s longtime rival Iran has been active within near neighbour Syria since civil war erupted a decade ago, with Tehran helping to prop up President Bashar al-Assad’s regime. Beginning in January 2013, Israel has periodically carried out attacks within Syria to counter Iranian entrenchment. Strikes have targeted Iranian and Syrian troops, as well as militias from multiple countries aligned with Tehran.
Airwars has tracked Israeli strikes in Syria for several years as part of its long running monitoring of actions there by all foreign actors. It has now published interactive mapping of all locally reported allegations against Israel in Syria. It’s believed to be the first comprehensive assessment of the civilian toll of an extensive but secretive air campaign.
Airwars researchers also recorded civilian harm from Israeli military strikes during the May 2021 eruption of violence in Gaza, alongside harm caused by rockets fired into Israel by Palestinian militants.
An image from Airwars’ interactive map of civilian harm in Gaza
Choice of targets
Since 2008 Israel and Palestinian militants in the Gaza Strip have fought four major combat operations. Airwars researchers looked at the latest conflict in May 2021 in order to provide comparative data with the more limited civilian harm events being reported from Israeli strikes in Syria.
After compiling all community-reported civilian harm events in the conflicts in Syria and Gaza, Airwars researchers found that one of the critical explainers behind the dramatically different outcomes for civilians was where the IDF chooses to bomb.
According to local reports, the great majority of Israeli actions in Syria have targeted military assets such as air bases, troop convoys and weapons stores, away from major cities and towns. Hundreds of militants were killed in these operations, for the most part in military settings.
In Gaza, the picture was very different. Strikes routinely hit residential neighbourhoods, and militants were frequently targeted in non-military settings: Airwars identified 17 locally reported incidents in which militants were targeted in residential buildings and in which civilians were killed or injured nearby. In those incidents, local reports found that between 27 and 33 civilians were killed, with more than 100 injured. One third of those killed in the Gaza Strip were children.
Airwars also identified between 56 and 68 civilians killed when the IDF targeted what they said was a Hamas militant tunnel network beneath heavily populated areas in Gaza City, leading the buildings above to collapse. Most of the deaths came from a single incident: in the early morning of May 16th, at least 41 civilians were killed in strikes on the residential al-Wahda street, of which up to 18 were children.
Riyad Ishkontana, 42, lost his wife and four of his children in the al-Wahda street attack. He had spent the days leading up to the bombing reassuring the young family they were safe: their building was in an area of professionals and shops, he told them. But in the early hours of the morning, as Ishkontana was out getting snacks, the building was hit. Only one of his children survived. “I wish I never left,” he told The New York Times.
Population density mapping
Airwars also mapped all civilian harm allegations in Gaza, Syria and Israel against population density, and found a second clear driver of civilian harm: the more heavily populated an area, the more civilians were killed.
Airwars’s new landing page comparing Israeli actions in Syria and Gaza
In Gaza, one of the most heavily populated places in the world, more than 1,500 declared Israeli air and artillery strikes hit the territory in just 11 days. This dramatically increased the likelihood of civilian harm. Even within Gaza, there was a clear trend – the more heavily populated a neighbourhood, the more civilians died there.
The trend was also noticeable in Syria. While the scale of civilian harm from IDF strikes was much lower than in Gaza, it is still overwhelmingly located in heavily populated areas. Around 45 percent of estimated civilian casualties from Israeli strikes since 2013 occurred in the capital Damascus. In Israel, 17 of the 33 reported civilian harm incidents resulting from Palestinian rockets also took place in more densely populated areas, Airwars found.
Population density in Gaza may have given some a false sense of security. On May 12th in Gaza, airstrikes killed Reema Saad, who was four months pregnant, alongside her two children and husband. The family had decided to stay in their apartment because they believed the densely populated neighbourhood would be immune from targeting, Reema’s mother Samia told Middle East Eye.
Airwars mapping of population density and reported civilian harm for Gaza, May 2021
Urban deaths part of a global trend
The new findings support what Airwars has found across all conflicts it monitors: that using wide area effect explosive weapons in populated urban areas leads to high levels of civilian deaths and injuries.
This phenomenon is certainly not restricted to actions by the IDF, or by Palestinian militant groups. Indeed, the Gaza campaign in particular can be seen as part of a profoundly worrying trend in which nations and others conduct intensive military actions in urban areas, often with devastating results.
High civilian casualties in Gaza are symptomatic of an escalating and troubling global military trend in the use of wide area effect weapons in populated areas (sometimes known as EWIPA) – seen from Gaza to Mosul, Aleppo to Raqqa, and Tripoli to Kabul. These latest findings lend further urgency to an ongoing international push to restrict their use in a United Nations-brokered Political Declaration by nations, expected to be finalised in early 2022.
“Our latest study corroborates what we have found with other large scale conflicts in Iraq, Syria and elsewhere: even technologically advanced militaries kill large numbers of civilians when attacks focus on urban centres,” Chris Woods, director at Airwars, said. “Despite repeated assurances to the contrary, it’s clear that ‘precision warfare’ cannot sufficiently mitigate civilian harm.”
“Stark differences in civilian deaths and injuries from Israeli actions in Syria and in the Gaza Strip clearly illustrate that the most significant driver of civilian harm remains the use of explosive weapons in populated areas. The single most effective way to reduce the number of civilians dying in warfare would be to restrict the use of such dangerous wide area effect weapons on urban centres.”
How the new research was carried out
The Airwars report is the result of months of meticulous research carried out by a team of local language researchers, geolocators and specialist assessors.
Thousands of local media, social media and official sources documenting civilian harm as it happened were identified and archived by Airwars’ team of Arabic-, Hebrew- and English-language researchers in relation to the May 2021 conflict in Gaza and Israel. Researchers also continue to monitor and archive all civilian harm allegations in Syria resulting from Israeli strikes since 2013.
Airwars has then assessed the civilian harm from each incident in Gaza, Syria and Israel using the same standard methodology it applies across all conflicts it monitors. Its approach can best be described as remote, original language hyperlocal monitoring of casualty claims by affected communities – along with a review of broader reports and claims by belligerents, media and other investigators. All assessments are viewed as provisional – that is, any credible new information relating to an event will be subsequently added, potentially affecting our understanding of the incident.
Full resource list
The full report available in English, Hebrew and Arabic
Interactive mapping of civilian harm in Gaza
Video documenting key findings
Full dataset for civilian harm from Israeli strikes in Gaza and Syria
Full dataset for civilian harm from Palestinian rocket fire in Israel
נפגעים אזרחיים מפעולות מילטינטיות פלסטיניות במאי 2021
الفصائل الفلسطينية في إسرائيل
Civilian Casualties from Palestinian Militant Actions May 2021
Residents of a Gaza apartment block recall the frantic minutes before their homes were turned to rubble
This article was originally published as an interactive piece in The Guardian, co-written and researched with the Airwars Investigations Unit. It later won an Amnesty Media Award.
During the 11-day war between Israel and Palestinian militants in May 2021, Israeli airstrikes destroyed five multi-storey towers in the heart of Gaza City. The images of buildings crumbling to the ground flashed across TV channels around the world as Gaza faced the most intense Israeli offensive since 2014. At least 256 Palestinians were killed, including 66 children, and 13 in Israel, including two children. Israel claimed it was destroying the military capabilities of Hamas, who had fired rockets at Israel after weeks of tension in Jerusalem over the planned displacement of Palestinian residents and police raids on al-Aqsa mosque during Ramadan.
Each time Israel said it was targeting Hamas and that it had warned the residents first. But what is it like to have only a few minutes to evacuate before watching your life collapse into rubble?
In conjunction with the civilian harm monitoring organisation Airwars, the Guardian spoke with dozens of residents and gathered footage and photos to piece together the story of one building, al-Jalaa tower, demolished by an Israeli airstrike on 15 May 2021. These are the stories from inside the tower, of the Mahdi clan, who owned and lived in the building, the Jarousha family and the Hussein family.
Incident date
May 20, 2021
LOCATION
بئر السبع, Beersheva, Southern, IsraelTwo civilians, including a child, were injured when a rocket, reportedly fired from Gaza, struck the city of Be’er Sheva, in southern Israel on May 20th 2021, according to multiple reports. Israel media outlet Behadrei Haredim said the Magen David Adom ambulance service attended to a 50-year-old man, injured to his legs, and a 14-year-old
Summary
Incident date
May 20, 2021
LOCATION
بئر السبع, Beersheba, Southern, IsraelA rocket struck a factory in an industrial area of Beersheba, Israel on May 20th, 2021 resulting in injuries, according to local reports. In a video posted by Al Jazeera Arabic several vehicles parked outside the factory were also seen to be damage. Images uploaded by Quds10 show damage to an exterior wall of the
Summary
Incident date
May 20, 2021
LOCATION
عسقلان, Ashkelon, Southern, IsraelA rocket fired by Al Qassam directly hit a home in Ashkelon, injuring two civilians and causing damage to the building and surrounding area. Al Qassam claimed responsibility for the attack in a Telegram post that stated at 12:59 “Al-Qassam Brigades bombard occupied Ashkelon with a missile launch” and added at 13:18 “The enemy admits that a [settler]
Summary
Incident date
May 20, 2021
LOCATION
بيري, Beeri, Southern, IsraelA man was injured in a reported Palestinian rocket attack on the Kibbutz of Be’eri in southern Israel, on May 20th 2021, according to local reports. The Magon David Adom ambulance service said its staff provided medical care to a 53-year-old man who was transported to hospital in a light condition. Walla News reported the
Summary
Incident date
May 19, 2021
LOCATION
أوفاكيم, Ofakim, Southern, IsraelOne person was injured when a rocket struck the city of Ofakim, southern Israel on May 19th 2021, according to local reports. Shihab news agency quoted “Hebrew sources” saying: “A settler was injured in Ofkim after the resistance fired a wave of missiles.” The Al Qassam Brigade claimed responsibility for the strike, according to Anadolu
Summary
Incident date
May 19, 2021
LOCATION
سديروت, Sderot, Southern, IsraelFive rockets were fired by Al Qassam into the city of Sderot, injuring at least two civilians on May 19, 2021. Al Qassam confirmed that they had attacked the city of Sderot that day. The rockets reportedly caused damage to several buildings and cars, according to multiple sources. It was reported that either two or
Summary
Incident date
May 19, 2021
LOCATION
عسقلان, Ashkelon, Southern, IsraelRockets fired by Al-Qassam hit the city of Ashkelon, reportedly leading to injuries for between six and eight civilians who fell whilst running to bomb shelters. Civilians were transferred to Barzillai Hospital for treatment. According to one source, around 5.30pm eight physically injured civilians arrived at Barzillai hospital including one victim who was injured in
Summary
Incident date
May 18, 2021
LOCATION
جنوب اسرائيل, Ohad, Southern, IsraelTwo Thai nationals were killed, and as many as 20 people injured, when a rocket reportedly fired by the Al-Qassam Brigades struck an agricultural packaging plant in the town of Ohad, in southern Israel on May 18th, 2021, according to local reports. The Al Qassam Brigade released a statement claiming responsibility for the strike in